The app market is big business, with applications dominating user behaviour since the maiden iPhone bought them to public attention. It’s often claimed that all companies need an app to be considered relevant and attract an audience in 2025.
What is often misunderstood is the length and breadth of apps available to consumers today. Apps are not limited to downloads from the relevant iOS and Google Play stores on a smartphone or tablet. Web apps are an exciting way to enhance the lives of users and bolster a business reputation alike.
Contents
A web app is, as you may have guessed by now, shorthand for a web application. A web app is often a form of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), working simultaneously on the client-side of hardware (i.e., a user computer) and server-side (within an internet browser or a cloud).
Examples of web apps include online shopping stores, e-learning platforms, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) sites, web-based homepages of social media sites, and content management systems (CMS) to create websites, such as WordPress.
Typically, web apps work through a command issued online, with changes simultaneously made on a computer, smartphone or other appliance. This is a four-step process that breaks down as follows.
If you want to use a web app for your business, you’ll first need to undertake web app development. This is a complicated procedure that may require specialist knowledge and experience. Do not assume that a traditional web developer or app developer will construct an appropriate web app.
The core difference between a website and a web app comes from the way users interact with them. A website is all about passive output. You may visit a website to check the weather or a sporting result, read a review of a product. Either way, the result is the same. You’ll absorb what the website has to offer. A web app is a little different. In addition to passively absorbing data from a web app, you’ll also directly interact with – and potentially edit – the contents. As much as a website is defined by output, a web app is primarily concerned with input.
Arguably the most significant benefit of a web app is the flexibility that it affords. A web app is both server- and client-based. This means that you can access data from anywhere with a web browser. This can bring a number of business benefits.
The most basic approach to web app development is to follow five main steps: Research, Design, Development, Testing and Launch.
Realistically, be prepared to pay at least £5,000 for a basic web app. The more bells and whistles that you look to add, the higher this bill will eventually rise.
What is a web app?
A web app is, as you may have guessed by now, shorthand for a web application. A web app is often a form of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), working simultaneously on the client-side of hardware (i.e., a user computer) and server-side (within an internet browser or a cloud).
Perhaps the most common example of a web app is an email account. In 2025, we’re all connected to our email 24/7, thanks to apps downloaded to our smartphones. However, if you send an email from a browser on a desktop computer, the results will be identical – and simultaneous – on your other devices.
Examples of web apps
Examples of web apps include:
- Online shopping stores, whether that’s a monolith like Amazon or a smaller, independent site
- Educational and e-learning platforms that require interaction
- Databases that can be edited and updated in real time
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) sites, like Basecamp
- Web-based homepages of social media networks
- Basic content management systems (CMS) to create websites, such as WordPress
Here are some further examples of web apps in action.
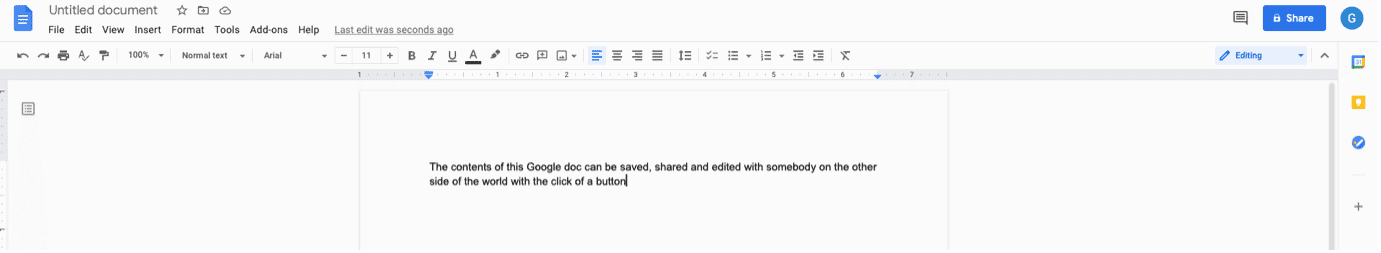
A Google Doc is a commonly used web app. These are a great way to share files without crippling an inbox with large attachments.
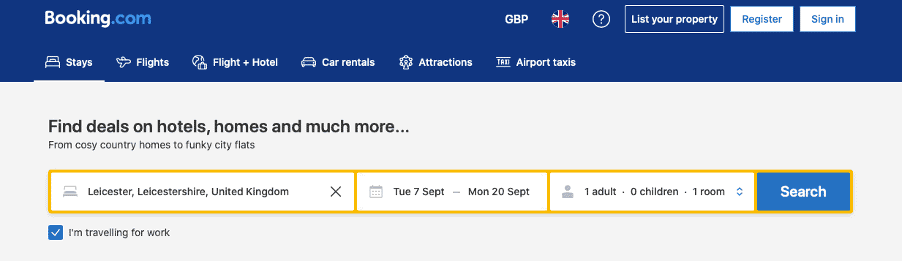
Fancy a trip to sunny Leicester to visit the Creative.onl offices? Any website that allows you to book travel and accommodation will actually be a web app.
How does a web app work?
Typically, web apps work through a command issued online, with changes simultaneously made on a computer, smartphone or other appliance. This is a four-step process that breaks down as follows.
As you’ll see, a web app can be a great way to approach real-time solutions across multiple platforms.
What is web app development?
If you want to use a web app for your business, you’ll first need to undertake web app development. This is a complicated procedure that may require specialist knowledge and experience. Do not assume that a traditional web developer or app developer will construct an appropriate web app. To successfully develop a web app, follow this 7-step guide.
How to develop a web application
- Identify a problem or pain point that many users may experience
And confirm if a web app is the best possible way to resolve this
- Create a theoretical mock-up
Of a solution that your web app will present – more about prototyping here.
- Engage with potential users of the web app
Ensuring they consider your plans to be user-friendly and effective.
- Construct a framework for the web app
The information architecture is key to the success of your product.
- Hire somebody to build and construct your web app
If you’d like to discuss how Creative.onl can help with this, feel free to contact us
- Build the web app according to the approved framework
And test it with users to confirm suitability.
- Launch your web app
And market it to your target audience, regularly reviewing and acting upon feedback
You can hire an external developer here or learn how to develop a web app yourself. Codeacademy offers a 7-day free trial if you’re prepared to devote the time to study in this short timeframe. Alternatively, Udemy has a cost-effective option that can be completed at your leisure.
There may be a measure of trial and error involved here. Do not be disheartened if a web app is not entirely successful at the first time of asking. Constant testing and improvements will eventually yield the results that you seek.
What’s the difference between a web app and a website?
A question you may be pondering is, “what’s the difference between a web app and a website?” After all, a web app takes longer to create than a website, at a more significant expense. You’d be forgiven for wondering where this extra money and effort is going.
The core difference between a website and a web app comes from the way users interact with them. A website is all about passive output. You may visit a website to check the weather or a sporting result, read a review of a new play or check out reviews of something you’re interested in purchasing. Either way, the result is the same. You’ll absorb what the website has to offer.
A web app is a little different. In addition to passively absorbing data from a web app, you’ll also directly interact with – and potentially edit – the contents. As much as a website is defined by output, a web app is primarily concerned with input. There’s room for both but ensure you understand that they offer distinctly different outcomes.
| What about progressive web applications? |
|---|
| A further wrinkle to this discussion is the progressive web app – an advancement on traditional web apps. You’ll find a complete guide to progressive web apps here, but in a nutshell, these are internet-based replicas of a smartphone app. Take Twitter, for example. The PWA of Twitter is impossible to distinguish from a native app found on a tablet or smartphone, where a traditional web app may differ in aesthetics and operation. |
Why would a business consider commissioning a web app?
We have just defined the difference between a web app, but the same question may still be hanging in the air. Why spend this extra money, and undertake a more challenging task than simply ordering the construction of a website?
Arguably the most significant benefit of a web app is the flexibility that it affords. As we mentioned at the top of this guide, a web app is both server- and client-based. This means that you can access data from anywhere with a web browser. This could be Safari, Chrome, Internet Explorer if you’re a traditionalist … any of the standard browsers that speak common coding languages.
This flexibility matters when it comes to updating an app. A client-based app will see data stored on a hard drive, such as on a particular computer. That’s fine if you can be sure that you’ll always have access to that hardware, but in the event of a problem, you’ll be stuck. In addition, if the computer experiences a major fault – or, heaven forbid, be stolen – you’ll find it increasingly difficult to update your app.
Of course, a web app will also provide the opportunity for greater connections. This may be optional, or it could be compulsory – that depends on your business model. If you’re looking to take payments from customers, for example, encourage commenting and interaction with pages, a web app is the way to go.
Finally, consider how a web app can be accessed by – theoretically – any user. By all means, develop a cross-platform app to cease any tiresome iOS vs Android debates. Such an approach is still reliant upon your clients making use of a smartphone or tablet, though. With a web app, you’ll potentially reach a far wider audience.
What is the best web app development process?
We touched briefly upon the process of creating a web app previously. If you’re going to commit to this process for your business, though, you’ll need to tackle the project in more detail. Let’s elaborate on how to construct the ideal web app.
Research
As with any undertaking, your first step will be to conduct some market research. Ask yourself a simple question – is a web app strictly necessary for your business? Is it worth spending the extra money, or are you better off sticking with a common or garden variety website?
If you do decide that a web app will meet your needs, the research does not end there. You’ll also need to investigate what your clients will be looking for. If you’re going to commit the time, effort and money to create a web app, you’ll be looking for an appropriate return on investment.
Design
Next comes the design process. Start by brainstorming potential solutions to the issue that you are looking to resolve. The more options you have at this juncture, the better. While you’re planning, there are no bad ideas.
Get these suggestions down on paper and start to consider the design for your app. You should involve potential users at this stage, as they will provide sufficient insights into how the app will need to work.
If you have the capability, create a wireframe for your web app at this stage. If you are filled with ideas but struggle with the execution, skip straight to finding an appropriate developer to create your web app.
Development
We have said this before, but a good point merits repeating. A web app is not the same as a website or a mobile app, and a particular skill set is required to develop it. Always ensure you find a freelancer or agency with the relevant abilities.
Beyond this, the process of finding the best possible developer is similar to any search for an app developer. Ensure you share chemistry with a potential partner and that you’re happy to undertake a long-term working relationship.
Testing
The final, and arguably most important, step before launch is to test your web app. Re-engage with the users that helped you design your app at this stage. These are your target audience, after all.
Keep testing the web app until you’re confident that it works as planned. You must complete sufficient test phases prior to launch. Iron out any flaws before users notice them. Negative reviews on sites like Trustpilot can seriously impact your business.
Launch
When you’re ready, launch your web app and ensure that the world is aware of what you have created. Keep an eye on your web app’s performance, ensuring that it is delivering what you anticipated.
What software, technologies and languages are commonly used to create web apps?
Web apps are built exclusively within a web server, so commonplace software is required. A web app can be created within a browser, with Google Chrome regarded as the most popular choice.
Everyday, popular programming language is used for the front end of web apps, most notably HTML, JavaScript and CSS. Of course, the functional backend will require a more advanced language like Python.
How much does web app development cost?
If you’re confident in your abilities to take on a DIY approach to creating a web app, the bills should not extend far beyond your education. Of course, you’ll also need to set aside the time required to complete the task and any expenses pertaining to market research.
If you decide to look outside your team, you can choose between a freelancer or an agency. A freelancer will be considerably cheaper, especially if you decide to write the web app in JavaScript. Expertise in this coding language typically attracts the lowest costs.
Alas, hiring a freelancer can be fraught with risk. You will be reliant on the availability and expertise of one individual and will have minimal comeback in the event of a future problem. An agency will boast a team of experienced developers, all of whom will bring their own abilities to the table.
So, to return to the question at hand, how much budget should be set aside for a web app? Realistically, be prepared to pay at least £5,000 for a basic web app. The more bells and whistles that you look to add, the higher this bill will eventually rise.
Ask for a transparent cost from a freelancer or agency, as it is easy to run up a charge well into five figures for this job. The expenses related to app development can quickly spiral if you do not keep an eye on them.